Michael.cowley82
Shared posts
{Ge9[Si(SiMe3)2(SiPh3)]3}−: Ligand Modification in Metalloid Germanium Cluster Chemistry
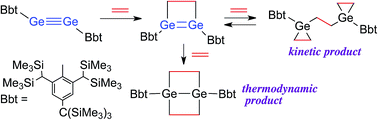
Reaction of a diaryldigermyne with ethylene
DOI: 10.1039/C5SC01266J, Edge Article
 Open Access
Open Access   This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.
  This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.
Reaction of a stable digermyne with ethylene afforded the corresponding 1,2-digermacyclobutene. Depending on the reaction conditions applied, further reaction of this 1,2-digermacyclobutene with ethylene furnished two different reaction products: a 1,4-digerma-bicyclo[2.2.0]hexane or a bis(germiranyl)ethane.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
1,2-Azaborine: The Boron-Nitrogen Derivative of ortho-Benzyne
Abstract
The BN analogue of ortho-benzyne, 1,2-azaborine, is generated by flash vacuum pyrolysis, trapped under cryogenic conditions, and studied by direct spectroscopic techniques. The parent BN aryne spontaneously binds N2 and CO2, thus demonstrating its highly reactive nature. The interaction with N2 is photochemically reversible. The CO2 adduct of 1,2-azaborine is a cyclic carbamate which undergoes photocleavage, thus resulting in overall CO2 splitting.

Azaborine in a flash: The boron–nitrogen derivative of ortho-benzyne, 1,2-azaborine, can be synthesized by flash vacuum pyrolysis (FVP) and trapped under cryogenic conditions to form a Lewis acid/base complex with nitrogen. Irradiation generates the free 1,2-azaborine which readily reacts with dinitrogen at slightly elevated temperatures.
An Isolable Radical Anion of an Organosilicon Cluster Containing Only σ Bonds
Abstract
The radical anion of octa-tert-butyloctasilacubane was generated and isolated. The EPR spectrum showed the satellites due to the tertiary 13C nuclei of the eight tert-butyl groups. The X-ray crystallographic analysis showed that the Si![[BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8ff.gif) Si bonds are shortened and the Si
Si bonds are shortened and the Si![[BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8ff.gif) C bonds are elongated compared with those of octa-tert-butyloctasilacubane. These results are well explained by the distribution of an unpaired electron in the singly occupied molecular orbital (SOMO).
C bonds are elongated compared with those of octa-tert-butyloctasilacubane. These results are well explained by the distribution of an unpaired electron in the singly occupied molecular orbital (SOMO).

The radical anion of octa-tert-butyloctasilacubane was generated and isolated (see picture). The X-ray crystallographic analysis showed that the Si![[BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8ff.gif) Si bonds are shortened and the Si
Si bonds are shortened and the Si![[BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8ff.gif) C bonds are elongated compared with those of octa-tert-butyloctasilacubane. These results are well explained by the distribution of an unpaired electron in the singly occupied molecular orbital (SOMO).
C bonds are elongated compared with those of octa-tert-butyloctasilacubane. These results are well explained by the distribution of an unpaired electron in the singly occupied molecular orbital (SOMO).
Biphilic Organophosphorus Catalysis: Regioselective Reductive Transposition of Allylic Bromides via PIII/PV Redox Cycling
Pentagermapyramidane: Crystallizing the “Transition-State” Structure
Abstract
The first example of the homonuclear pyramidanes, pentagermapyramidane, was synthesized, fully characterized, and computationally studied to reveal its peculiar structural features and the nature of its apex-to-base bonding interactions. Both solid-state and solution structures of pentagermapyramidane are discussed based on the computed stabilities of its square-pyramidal and distorted forms.

Germanium pyramids: The homonuclear pentagermapyramidane Ge[Ge4(SiMetBu2)4] (1) was synthesized and characterized. Crystal structures of two structural variations of 1 are reported: the distorted pyramidal structure 1 a, corresponding to the energy minima on the Ge5R4 potential energy surface (PES), and the square-planar pyramidal 1 b, representing a transition state on the PES.
One-Step Synthesis of a [20]Silafullerane with an Endohedral Chloride Ion
Michael.cowley82incredible
Abstract
Silicon analogues of the most prominent carbon nanostructures, namely, hollow spheroidals such as C60 and the fullerene family, have been unknown to date. Herein we show that discrete Si20 dodecahedra, stabilized by an endohedral guest and valence saturation, are accessible in preparative yields through a chloride-induced disproportionation reaction of hexachlorodisilane in the presence of tri(n-butyl)amine. X-ray crystallography revealed that each silicon dodecahedron contains an endohedral chloride ion that imparts a net negative charge. Eight chloro substituents and twelve trichlorosilyl groups are attached to the surface of each cluster in a strictly regioregular arrangement, a thermodynamically preferred substitution pattern according to quantum-chemical assessment. Our results demonstrate that the wet-chemical self-assembly of a complex, monodisperse Si nanostructure is possible under mild conditions starting from simple Si2 building blocks.

As simple as this: A stable, crystalline [20]silafullerane forms in preparatively useful yields through wet-chemical self-assembly from Si2Cl6 and chloride ions in the presence of an amine. Each silicon dodecahedron contains an endohedral chloride ion that imparts a net negative charge. Eight chloro substituents and twelve trichlorosilyl groups are attached to the surface of each cluster in a strictly regioregular arrangement.
Reactivity of Boryl- and Silyl-Substituted Carbenoids toward Alkynes: Insertion and Cycloaddition Chemistry
Nickel-Triad Complexes of a Side-on Coordinating Distannene
Abstract
NHC adducts of the stannylene Trip2Sn (Trip=2,4,6-triisopropylphenyl) were reacted with zero-valent Ni, Pd, and Pt precursor complexes to cleanly yield the respective metal complexes featuring a three-membered ring moiety Sn-Sn-M along with carbene transfer onto the metal and complete substitution of the starting ligands. Thus the easily accessible NHC adducts to stannylenes are shown to be valuable precursors for transition-metal complexes with an unexpected Sn![[BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8ff.gif) Sn bond. The complexes have been studied by X-ray diffraction and NMR spectroscopy as well as DFT calculations. The compounds featuring the structural motif of a distannametallacycle comprised of a [(NHC)2M0] fragment and Sn2Trip4 represent rare higher congeners of the well-known olefin complexes. DFT calculations indicate the presence of a π-type Sn–Sn interaction in these first examples for acyclic distannenes symmetrically coordinating to a zero-valent transition metal.
Sn bond. The complexes have been studied by X-ray diffraction and NMR spectroscopy as well as DFT calculations. The compounds featuring the structural motif of a distannametallacycle comprised of a [(NHC)2M0] fragment and Sn2Trip4 represent rare higher congeners of the well-known olefin complexes. DFT calculations indicate the presence of a π-type Sn–Sn interaction in these first examples for acyclic distannenes symmetrically coordinating to a zero-valent transition metal.

Differing analogues: On reacting the carbene adduct of the stannylene [Trip2Sn] (Trip=2,4,6-triisopropylphenyl) with zero-valent Group 10 complexes, symmetrically coordinating complexes of the distannene [Sn2Trip4] to Ni, Pd, and Pt have been obtained. Their structural and spectroscopic properties are presented and discussed.
Linking Deltahedral Zintl Clusters with Conjugated Organic Building Blocks: Synthesis and Characterization of the Zintl Triad [R-Ge9-CHCHCHCH-Ge9-R]4−
Abstract
The accessibility of triads with deltahedral Zintl clusters in analogy to fullerene–linker–fullerene triads is another example for the close relationship between fullerenes and Zintl clusters. The compound {[K(2.2.2-crypt)]4[RGe9-CH![[DOUBLE BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8fe.gif) CH
CH![[BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8ff.gif) CH
CH![[DOUBLE BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8fe.gif) CH-Ge9R]}(toluene)2 (R=(2Z,4E)-7-amino-5-aza-hepta-2,4-dien-2-yl), containing two deltahedral [Ge9] clusters linked by a conjugated (1Z,3Z)-buta-1,3-dien-1,4-diyl bridge, was synthesized through the reaction of 1,4-bis(trimethylsilyl)butadiyne with K4Ge9 in ethylenediamine and crystallized after the addition of 2.2.2-cryptand and toluene. The compound was characterized by single-crystal structure analysis as well asNMR and IR spectroscopy.
CH-Ge9R]}(toluene)2 (R=(2Z,4E)-7-amino-5-aza-hepta-2,4-dien-2-yl), containing two deltahedral [Ge9] clusters linked by a conjugated (1Z,3Z)-buta-1,3-dien-1,4-diyl bridge, was synthesized through the reaction of 1,4-bis(trimethylsilyl)butadiyne with K4Ge9 in ethylenediamine and crystallized after the addition of 2.2.2-cryptand and toluene. The compound was characterized by single-crystal structure analysis as well asNMR and IR spectroscopy.

Zintl triads: The general possibility to synthesize electronically coupled Zintl clusters using conjugated electron π-systems as linkers in analogy to fullerene–linker–fullerene triads opens a new area of applications for Zintl clusters.
Addition of Ethylene or Hydrogen to a Main-Group Metal Cluster under Mild Conditions
Abstract
Reaction of the tin cluster Sn8(Ar )4 (Ar
)4 (Ar =C6H2-2,6-(C6H3-2,4,6-Me3)2) with excess ethylene or dihydrogen at 25 °C/1 atmosphere yielded two new clusters that incorporated ethylene or hydrogen. The reaction with ethylene yielded Sn4(Ar
=C6H2-2,6-(C6H3-2,4,6-Me3)2) with excess ethylene or dihydrogen at 25 °C/1 atmosphere yielded two new clusters that incorporated ethylene or hydrogen. The reaction with ethylene yielded Sn4(Ar )4(C2H2)5 that contained five ethylene moieties bridging four aryl substituted tin atoms and one tin–tin bond. Reaction with H2 produced a cyclic tin species of formula (Sn(H)Ar
)4(C2H2)5 that contained five ethylene moieties bridging four aryl substituted tin atoms and one tin–tin bond. Reaction with H2 produced a cyclic tin species of formula (Sn(H)Ar )4, which could also be synthesized by the reaction of {(Ar
)4, which could also be synthesized by the reaction of {(Ar )Sn(μ-Cl)}2 with DIBAL-H. These reactions represent the first instances of direct reactions of isolable main-group clusters with ethylene or hydrogen under mild conditions. The products were characterized in the solid state by X-ray diffraction and IR spectroscopy and in solution by multinuclear NMR and UV/Vis spectroscopies. Density functional theory calculations were performed to explain the reactivity of the cluster.
)Sn(μ-Cl)}2 with DIBAL-H. These reactions represent the first instances of direct reactions of isolable main-group clusters with ethylene or hydrogen under mild conditions. The products were characterized in the solid state by X-ray diffraction and IR spectroscopy and in solution by multinuclear NMR and UV/Vis spectroscopies. Density functional theory calculations were performed to explain the reactivity of the cluster.

Tinned small molecules: Reactions of the tin cluster Sn8(Ar )4 under mild conditions yields two new insertion compounds from incorporation of ethylene (see picture; left) or H2 (right; Sn blue, C gray). To our knowledge, these are the first reactions between a stable main-group cluster and small molecules.
)4 under mild conditions yields two new insertion compounds from incorporation of ethylene (see picture; left) or H2 (right; Sn blue, C gray). To our knowledge, these are the first reactions between a stable main-group cluster and small molecules.
A Nuclear Singlet Lifetime of More than One Hour in Room-Temperature Solution
Abstract
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are supremely important techniques with numerous applications in almost all branches of science. However, until recently, NMR methodology was limited by the time constant T1 for the decay of nuclear spin magnetization through contact with the thermal molecular environment. Long-lived states, which are correlated quantum states of multiple nuclei, have decay time constants that may exceed T1 by large factors. Here we demonstrate a nuclear long-lived state comprising two 13C nuclei with a lifetime exceeding one hour in room-temperature solution, which is around 50 times longer than T1. This behavior is well-predicted by a combination of quantum theory, molecular dynamics, and quantum chemistry. Such ultra-long-lived states are expected to be useful for the transport and application of nuclear hyperpolarization, which leads to NMR and MRI signals enhanced by up to five orders of magnitude.

A long-lived nuclear singlet: A molecular system based on a 13C2-labelled naphthalene core has been designed to support long-lived nuclear singlet order in solution. A nuclear singlet lifetime exceeding one hour has been achieved in room-temperature solution.
A Phosphetane Catalyzes Deoxygenative Condensation of α-Keto Esters and Carboxylic Acids via PIII/PVO Redox Cycling
Isolation and Structural Characterization of Geminal Di(iodozincio)methane Complexes Stabilized with Nitrogen Ligands
Intramolecular Frustrated Lewis Pair with the Smallest Boryl Site: Reversible H2 Addition and Kinetic Analysis
Abstract
Ansa-aminoborane 1 (ortho-TMP![[BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8ff.gif) C6H4
C6H4![[BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8ff.gif) BH2; TMP=2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperid-1-yl), a frustrated Lewis pair with the smallest possible Lewis acidic boryl site (
BH2; TMP=2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperid-1-yl), a frustrated Lewis pair with the smallest possible Lewis acidic boryl site (![[BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8ff.gif) BH2), is prepared. Although it is present in quenched forms in solution, and BH2 represents an acidic site with reduced hydride affinity, 1 reacts with H2 under mild conditions producing ansa-ammonium trihydroborate 2. The thermodynamic and kinetic features as well as the mechanism of this reaction are studied by variable-temperature NMR spectroscopy, spin-saturation transfer experiments, and DFT calculations, which provide comprehensive insight into the nature of 1.
BH2), is prepared. Although it is present in quenched forms in solution, and BH2 represents an acidic site with reduced hydride affinity, 1 reacts with H2 under mild conditions producing ansa-ammonium trihydroborate 2. The thermodynamic and kinetic features as well as the mechanism of this reaction are studied by variable-temperature NMR spectroscopy, spin-saturation transfer experiments, and DFT calculations, which provide comprehensive insight into the nature of 1.

As simple as that: An intramolecular frustrated Lewis pair that consists of a very simple acidic boryl site (BH2) and a bulky amino group is found to split dihydrogen in a fast and reversible process. Spin-saturation transfer NMR techniques were used to measure the reaction rates and to obtain accurate kinetic parameters.
Influence of Ligand Modifications on Structural and Spectroscopic Properties in Terphenyl Based Heavier Group 14 Carbene Homologues
The Reactivities of Iminoboranes with Carbenes: BN Isosteres of Carbene–Alkyne Adducts
Abstract
The first examples of adducts of cyclic alkyl(amino) carbenes (CAAC) and N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) with iminoboranes have been synthesized and isolated at low temperature (−45 °C). The adducts show short B![[DOUBLE BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8fe.gif) N bonds and planarity at boron, mimicking the structures of the isoelectronic imine functionality. When di-tert-butyliminoborane was reacted with 1,3-bis(isopropyl)imidazol-2-ylidene (IPr), the initially formed Lewis acid–base adduct quickly rearranged to form a new carbene substituted with an aminoborane at the 4-position. Warming the iminoborane–CAAC adduct to room temperature resulted in an intramolecular cyclization to give a bicyclic 1,2-azaborilidine compound.
N bonds and planarity at boron, mimicking the structures of the isoelectronic imine functionality. When di-tert-butyliminoborane was reacted with 1,3-bis(isopropyl)imidazol-2-ylidene (IPr), the initially formed Lewis acid–base adduct quickly rearranged to form a new carbene substituted with an aminoborane at the 4-position. Warming the iminoborane–CAAC adduct to room temperature resulted in an intramolecular cyclization to give a bicyclic 1,2-azaborilidine compound.

A B in C’s clothing: The isolation and characterization of a set of carbene adducts of iminoboranes indicates diverse reactivity patterns. Simple adducts present “boraimine” structures, which mimic the organic imine functionality. Rearrangements of these simple adducts yield backbone-substituted carbenes as well as 1,2-azaborolidines.
Reversible Intermolecular E–H Oxidative Addition to a Geometrically Deformed and Structurally Dynamic Phosphorous Triamide
Metal-Free σ-Bond Metathesis in Ammonia Activation by a Diazadiphosphapentalene
Electron-Induced Conversion of Silylones to Six-Membered Cyclic Silylenes
Toward Molecular Recognition: Three-Point Halogen Bonding in the Solid State and in Solution
Metal-Free σ-Bond Metathesis in 1,3,2-Diazaphospholene-Catalyzed Hydroboration of Carbonyl Compounds
Michael.cowley82check out the undergraduate project handbook...
Abstract
The first metal-free catalytic hydroboration of carbonyl derivatives has been developed in which a catalytic amount of 1,3,2-diazaphospholene effectively promotes a hydroboration reaction of aliphatic and aromatic aldehydes and ketones. The reaction mechanism involves the cleavage of both the P![[BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8ff.gif) O bond of the alkoxyphosphine intermediate and the B
O bond of the alkoxyphosphine intermediate and the B![[BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8ff.gif) H bond of pinacolborane as well as the formation of P
H bond of pinacolborane as well as the formation of P![[BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8ff.gif) H and B
H and B![[BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8ff.gif) O bonds. Thus, the reaction proceeds through a non-metal σ-bond metathesis. Kinetic and computational studies suggest that the σ-bond metathesis occurred in a stepwise but nearly concerted manner.
O bonds. Thus, the reaction proceeds through a non-metal σ-bond metathesis. Kinetic and computational studies suggest that the σ-bond metathesis occurred in a stepwise but nearly concerted manner.

Leave the metal out: A catalytic amount of diazaphospholene effectively promotes a hydroboration reaction of various aldehydes and ketones under metal-free conditions. Kinetic and computational studies show that the reaction mechanism involves a σ-bond metathesis process occurring in a stepwise but nearly concerted manner.
N-Heterocyclic CarbeneMain-Group Chemistry: A Rapidly Evolving Field
Phosphine complexes of lone pair bearing Lewis acceptors
DOI: 10.1039/C4DT02789B, Perspective
The unique structural outcomes and reactivity modes for phosphine complexes featuring lone-pair bearing acceptors are considered.
To cite this article before page numbers are assigned, use the DOI form of citation above.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
The influence of Michael Lappert on the chemistry landscape
DOI: 10.1039/C4DT90167C, Editorial
In memory of Michael F. Lappert, this Editorial introduces a collection of his most highly cited Royal Society of Chemistry publications, curated by members of the Dalton Transactions and ChemComm Editorial Boards.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Isolation of a Three-Coordinate Boron Cation with a Boron–Sulfur Double Bond
Abstract
The reaction of the bulky bis(imidazolin-2-iminato) ligand precursor (1,2-(LMesNH)2-C2H4)[OTs]2 (12+ 2[OTs]−; LMes=1,3-dimesityl imidazolin-2-ylidene, OTs=p-toluenesulfonate) with lithium borohydride yields the boronium dihydride cation (1,2-(LMesN)2-C2H4)BH2[OTs] (2+ [OTs]−). The boronium cation 2+ [OTs]− reacts with elemental sulfur to give the thioxoborane salt (1,2-(LMesN)2-C2H4)BS[OTs] (3+ [OTs]−). The hitherto unknown compounds 12+ 2[OTs]−, 2+ [OTs]−, and 3+ [OTs]− were fully characterized by spectroscopic methods and single-crystal X-ray diffraction. Moreover, DFT calculations were carried out to elucidate the bonding situation in 2+ and 3+. The theoretical, as well as crystallographic studies reveal that 3+ is the first example for a stable cationic complex of three-coordinate boron that bears a B![[DOUBLE BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8fe.gif) S double bond.
S double bond.

A healthy relationship: The first three-coordinate boron cation with a boron–sulfur double bond has the shortest B![[BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8ff.gif) S distance reported for a molecular complex. In the calculated LUMO, the contribution from the boron center confirms that the compound is a boron-centered cation. The HOMO−1 reveals the π interaction which is the cause of the close contact between B and S.
S distance reported for a molecular complex. In the calculated LUMO, the contribution from the boron center confirms that the compound is a boron-centered cation. The HOMO−1 reveals the π interaction which is the cause of the close contact between B and S.
Synthesis and Reactivity of a CAAC–Aminoborylene Adduct: A Hetero-Allene or an Organoboron Isoelectronic with Singlet Carbenes
Abstract
A one-electron reduction of a cyclic (alkyl)(amino)carbene (CAAC)–bis(trimethylsilyl)aminodichloroborane adduct leads to a stable aminoboryl radical. A second one-electron reduction gives rise to a CAAC–aminoborylene adduct, which features an allenic structure. However, in manner similar to that of stable electrophilic singlet carbenes, this compound activates small molecules, such as CO and H2.

Boron can do it! The first carbene that was stable at room temperature had a pseudo allenic structure, but owing to its high flexibility, it featured classical carbene reactivity. Similarly, a stable boron compound, isoelectronic with singlet carbenes, has an allenic structure, and is able to activate CO and H2.
Ag[Fe(CO)5]2+: A Bare Silver Complex with Fe(CO)5 as a Ligand
Abstract
Attempts to prepare Fe(CO)5+ from Ag[Al(ORF)4] (RF=C(CF3)3) and Fe(CO)5 in CH2Cl2 yielded the first complex of a neutral metal carbonyl bound to a simple metal cation. The Ag[Fe(CO)5]2+ cation consists of two Fe(CO)5 molecules coordinating Ag+ in an almost linear fashion. The ν(CO) modes are blue-shifted compared to Fe(CO)5, with one band above 2143 cm−1 indicating that back-bonding is heavily decreased in the Ag[Fe(CO)5]2+ cation.

Oxidation or coordination? A simple reaction between a silver salt with a weakly coordinating anion and Fe(CO)5 yields the unprecedented Ag[Fe(CO)5]2+ complex. This nonclassical carbonyl cation shows unusual stability as a crystalline solid (up to 150 °C). In the crystal and in DFT calculations it shows a unique bonding pattern with four carbonyl groups with bonds bent towards Ag, breaking the expected 4-fold symmetry.
N-Heterocyclic Carbene–Phosphinidyne Transition Metal Complexes
Michael.cowley82good synthon for 'NHC-P' fragment
Abstract
The N-heterocyclic carbene–phosphinidene adduct IPr![[DOUBLE BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8fe.gif) PSiMe3 is introduced as a synthon for the preparation of terminal carbene–phosphinidyne transition metal complexes of the type [(IPr
PSiMe3 is introduced as a synthon for the preparation of terminal carbene–phosphinidyne transition metal complexes of the type [(IPr![[DOUBLE BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8fe.gif) P)MLn] (MLn=(η6-p-cymene)RuCl) and (η5-C5Me5)RhCl). Their spectroscopic and structural characteristics, namely low-field 31P NMR chemical shifts and short metal–phosphorus bonds, show their similarity with arylphosphinidene complexes. The formally mononegative IPr
P)MLn] (MLn=(η6-p-cymene)RuCl) and (η5-C5Me5)RhCl). Their spectroscopic and structural characteristics, namely low-field 31P NMR chemical shifts and short metal–phosphorus bonds, show their similarity with arylphosphinidene complexes. The formally mononegative IPr![[DOUBLE BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8fe.gif) P ligand is also capable of bridging two or three metal atoms as demonstrated by the preparation of bi- and trimetallic RuAu, RhAu, Rh2, and Rh2Au complexes.
P ligand is also capable of bridging two or three metal atoms as demonstrated by the preparation of bi- and trimetallic RuAu, RhAu, Rh2, and Rh2Au complexes.

IPr![[DOUBLE BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8fe.gif) PSiMe3, an N-heterocyclic carbene–phosphinidene adduct, is used as a synthon for the preparation of terminal carbene–phosphinidyne transition metal complexes of the type [(IPr
PSiMe3, an N-heterocyclic carbene–phosphinidene adduct, is used as a synthon for the preparation of terminal carbene–phosphinidyne transition metal complexes of the type [(IPr![[DOUBLE BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8fe.gif) P)MLn]. These complexes exhibit spectroscopic and structural characteristics similar to those of arylphosphinidene complexes. The IPr
P)MLn]. These complexes exhibit spectroscopic and structural characteristics similar to those of arylphosphinidene complexes. The IPr![[DOUBLE BOND]](http://onlinelibrarystatic.wiley.com/undisplayable_characters/00f8fe.gif) P ligand is also capable of bridging two or three metal atoms, e.g., in bi- and trimetallic RuAu, RhAu, Rh2, and Rh2Au complexes.
P ligand is also capable of bridging two or three metal atoms, e.g., in bi- and trimetallic RuAu, RhAu, Rh2, and Rh2Au complexes.