Shared posts
[ASAP] Toward the Proactive Design of Sustainable Chemicals: Ionic Liquids as a Prime Example
Enzyme Conformation Influences the Performance of Lipase‐powered Nanomotors

The impact of enzyme orientation on the performance of lipase‐powered nanomotors was explored and analysed, indicating that hydrophobic interaction is the best strategy for immobilizing lipase to provide high‐efficiency catalysis. This results in high‐efficiency enhanced Brownian motion, which would be vital in promoting the future applications of enzyme‐powered micro/nanomotors.
Abstract
Enzyme‐powered micro/nanomotors have myriads of potential applications in various areas. To efficiently reach those applications, it is necessary and critical to understand the fundamental aspects affecting the motion dynamics. Herein, we explored the impact of enzyme orientation on the performance of lipase‐powered nanomotors by tuning the lipase immobilization strategies. The influence of the lipase orientation and lid conformation on substrate binding and catalysis was analyzed using molecular dynamics simulations. Besides, the motion performance indicates that the hydrophobic binding (via OTES) represents the best orienting strategy, providing 48.4 % and 95.4 % increase in diffusion coefficient compared to hydrophilic binding (via APTES) and Brownian motion (no fuel), respectively (with C [triacetin] of 100 mm). This work provides vital evidence for the importance of immobilization strategy and corresponding enzyme orientation for the catalytic activity and in turn, the motion performance of nanomotors, and is thus helpful to future applications.
[ASAP] Metal-Assisted and Solvent-Mediated Synthesis of Two-Dimensional Triazine Structures on Gram Scale

Cleaner enzymatic production of biodiesel with easy separation procedures triggered by a biocompatible hydrophilic ionic liquid
DOI: 10.1039/C9GC03796A, Paper
A biocompatible and hydrophilic ionic liquid was found to efficiently promote the enzymatic production of biodiesel with excellent yields from different oil resources.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
[ASAP] Self-Assembly of Copolymer Micelles: Higher-Level Assembly for Constructing Hierarchical Structure

[ASAP] Fabricating Covalent Organic Framework Capsules with Commodious Microenvironment for Enzymes

[ASAP] Heterogeneously Chemo/Enzyme-Functionalized Porous Polymeric Catalysts of High-Performance for Efficient Biodiesel Production

Morphogenesis of Metal–Organic Mesocrystals Mediated by Double Hydrophilic Block Copolymers
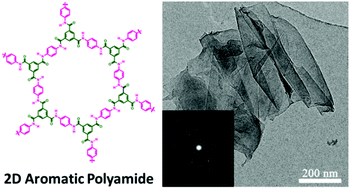
Mechanochemical synthesis of two-dimensional aromatic polyamides
DOI: 10.1039/C7CC02648J, Communication
2D aromatic polyamides (2DAPAs) were synthesized for the first time via a facile mechanochemical route under solvent-free and room temperature conditions.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Heterogeneous Catalysis in Zeolites, Mesoporous Silica, and Metal–Organic Frameworks
Crystalline porous materials are important in the development of catalytic systems with high scientific and industrial impact. Zeolites, ordered mesoporous silica, and metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) are three types of porous materials that can be used as heterogeneous catalysts. This review focuses on a comparison of the catalytic activities of zeolites, mesoporous silica, and MOFs. In the first part of the review, the distinctive properties of these porous materials relevant to catalysis are discussed, and the corresponding catalytic reactions are highlighted. In the second part, the catalytic behaviors of zeolites, mesoporous silica, and MOFs in four types of general organic reactions (acid, base, oxidation, and hydrogenation) are compared. The advantages and disadvantages of each porous material for catalytic reactions are summarized. Conclusions and prospects for future development of these porous materials in this field are provided in the last section. This review aims to highlight recent research advancements in zeolites, ordered mesoporous silica, and MOFs for heterogeneous catalysis, and inspire further studies in this rapidly developing field.

The similarities and differences in catalytic behavior of zeolites, mesoporous silica, and metal–organic frameworks in four types of general organic reactions (acid, base, oxidation, and hydrogenation) are discussed herein. The advantages and disadvantages of each porous material for particular catalytic reactions are highlighted. Future developments of the three types of porous materials in heterogeneous catalysis are also discussed.
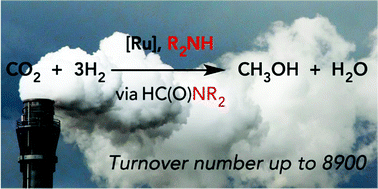
Highly productive CO2 hydrogenation to methanol - a tandem catalytic approach via amide intermediates
DOI: 10.1039/C7CC04613H, Communication
Amines to an end - homogeneous ruthenium catalysts based on mixed donor P-N ligands with a range of amine auxiliaries are highly productive for CO2 reduction to methanol, the nature of this amine having a profound effect on performance.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Development of a Cambridge Structural Database Subset: A Collection of Metal–Organic Frameworks for Past, Present, and Future
Impact of Shape Persistence on the Porosity of Molecular Cages
Controlled Encapsulation of Functional Organic Molecules within Metal–Organic Frameworks: In Situ Crystalline Structure Transformation

Functional organic molecules/metal–organic frameworks composites can be obtained by in situ crystalline structure transformation from ZIF-L to ZIF-8-L under double solvent conditions. Interestingly, the as-prepared molecules/ZIF-8-L composites with the leaf-like morphology exhibit good fluorescence properties and size selectivity in fluorescent quenchers due to the molecular sieving effect of the well-defined microporous ZIF-8-L.
Experimental and Theoretical Understanding of Nitrogen-Doping-Induced Strong Metal–Support Interactions in Pd/TiO2 Catalysts for Nitrobenzene Hydrogenation

Application of Ionic Liquids to Energy Storage and Conversion Materials and Devices
Catalytically active designer crown-jewel Pd-based nanostructures encapsulated in metal-organic frameworks
DOI: 10.1039/C6CC09270E, Communication
A series of Pd based bimetallic NPs with unique "crown-jewel" structure and tunable composition have been successfully fabricated inside the MOF pores, exhibiting superior catalytic activity and stability.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Water-Mediated Mars–Van Krevelen Mechanism for CO Oxidation on Ceria-Supported Single-Atom Pt1 Catalyst

Ionic Flash NanoPrecipitation (iFNP) for the Facile, One-Step Synthesis of Inorganic-Organic Hybrid Nanoparticles in Water
DOI: 10.1039/C6NR09364G, Communication
Ionic Flash NanoPrecipitation (iFNP) was evaluated as a novel method for the synthesis of inorganic-organic hybrid nanomaterials and proved to be remarkably effective, fast and practical. To prove the potential...
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Humidity- and Photo-Induced Mechanical Actuation of Cross-Linked Liquid Crystal Polymers

Azobenzene-containing cross-linked liquid crystal polymer films without hydrophilic groups exhibit dual-responsivity to humidity and UV light. The films realize not only a series of large and sophisticated contactless motions by utilizing moisture, including an inchworm walk, and tumbling locomotion, but also dual-mode actuation that can be applied in flexible electronics.
Supported Aluminum Catalysts for Olefin Hydrogenation

Hexaaminobenzene as a building block for a Family of 2D Coordination Polymers
Synchronized Offset Stacking: A Concept for Growing Large-Domain and Highly Crystalline 2D Covalent Organic Frameworks
Porous Peapod Structured Pd Nanopaticles Catalysts with Super Stability and High Efficiency
DOI: 10.1039/C6CC08598A, Communication
Porous peapod structured Pd@m-C/SiO2 nanostructures were prepared by a nanoconfinment method. For this peapod structure, Pd nanoparticles showed high efficiency and stability for the chemical reactions, such as reduction of...
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Selective Formic Acid Dehydrogenation on Pt-Cu Single-Atom Alloys

A Modulator-Induced Defect-Formation Strategy to Hierarchically Porous Metal–Organic Frameworks with High Stability
Abstract
The pore size enlargement and structural stability have been recognized as two crucial targets, which are rarely achieved together, in the development of metal–organic frameworks (MOFs). Herein, we have developed a versatile modulator-induced defect-formation strategy, in the presence of monocarboxylic acid as a modulator and an insufficient amount of organic ligand, successfully realizing the controllable synthesis of hierarchically porous MOFs (HP-MOFs) with high stability and tailorable pore characters. Remarkably, the integration of high stability and large mesoporous property enables these HP-MOFs to be important porous platforms for applications involving large molecules, especially in catalysis.

Cause and defect: Pore size enlargement and structural stability are two crucial targets but hardly achieved together in metal–organic frameworks (MOFs). A versatile modulator-induced defect-formation strategy has been developed to provide hierarchically porous MOFs (HP-MOFs) with high stability and tailorable pore characters, which are important porous platforms for large-molecule applications, especially in catalysis.
Chemical Conversion of Linkages in Covalent Organic Frameworks
Catalysis by Supported Single Metal Atoms