04 Sep 10:22
Nanoscale, 2019, 11,17065-17072
DOI: 10.1039/C9NR06358G, Paper
Peijian Wang, Siyuan Luo, Lincoln Boyle, Hao Zeng, Shaoming Huang
We report controlled fractal growth of atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs) by chemical vapor deposition, with morphological evolution from dendritic to triangular.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry

21 Aug 10:15
by Arelo O. A Tanoh†‡, Jack Alexander-Webber§, James Xiao†, Ge´raud Delport†, Cyan A. Williams‡?, Hope Bretscher†, Nicolas Gauriot†, Jesse Allardice†, Raj Pandya†, Ye Fan§, Zhaojun Li†, Silvia Vignolini?, Samuel D. Stranks†, Stephan Hofmann§, and Akshay Rao†*

Nano Letters
DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b02431

14 Aug 10:42
Dalton Trans., 2019, 48,12822-12827
DOI: 10.1039/C9DT01872G, Communication
Brian S. Chapman, Sumeet R. Mishra, Joseph B. Tracy
TiO2 nanofibers with average diameters of ∼70 nm were prepared by direct electrospinning.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry

05 Mar 18:18
by Hui Xu, Xinchang Pang, Yanjie He, Ming He, Jaehan Jung, Haiping Xia, Zhiqun Lin
Abstract
We developed an unconventional route to produce uniform and intimately contacted semiconducting organic–inorganic nanocomposites for potential applications in thermoelectrics. By utilizing amphiphilic star-like PAA-b-PEDOT diblock copolymer as template, monodisperse PEDOT-functionalized lead telluride (PbTe) nanoparticles were crafted via the strong coordination interaction between PAA blocks of star-like PAA-b-PEDOT and the metal moieties of precursors (i.e., forming PEDOT–PbTe nanocomposites). As the inner PAA blocks are covalently connected to the outer PEDOT blocks, the PEDOT chains are intimately and permanently tethered on the PbTe nanoparticle surface, thereby affording a well-defined PEDOT/PbTe interface, which prevents the PbTe nanoparticles from aggregation, and more importantly promotes the long-term stability of PEDOT–PbTe nanocomposites. We envision that the template strategy is general and robust, and offers easy access to other conjugated polymer–inorganic semiconductor nanocomposites for use in a variety of applications.

A robust strategy to produce spherically shaped organic–inorganic nanocomposites composed of PbTe nanoparticles tethered with poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) chains was developed by using amphiphilic star-like diblock copolymer PAA-b-PEDOT as template. The PbTe–PEDOT nanohybrids show long-term stability and hold promise for use in thermoelectrics.
09 Feb 22:46
by Yi-Yang Sun, Michael L. Agiorgousis, Peihong Zhang and Shengbai Zhang

Nano Letters
DOI: 10.1021/nl504046x

09 Feb 22:42
by Dongju Lee, Bin Lee, Kwang Hyun Park, Ho Jin Ryu, Seokwoo Jeon and Soon Hyung Hong

Nano Letters
DOI: 10.1021/nl504397h

09 Feb 16:35
by Regine Gries, Robert Britton, Michael Holmes, Huimin Zhai, Jason Draper, Gerhard Gries
Abstract
Bed bugs have become a global epidemic and current detection tools are poorly suited for routine surveillance. Despite intense research on bed bug aggregation behavior and the aggregation pheromone, which could be used as a chemical lure, the complete composition of this pheromone has thus far proven elusive. Here, we report that the bed bug aggregation pheromone comprises five volatile components (dimethyl disulfide, dimethyl trisulfide, (E)-2-hexenal, (E)-2-octenal, 2-hexanone), which attract bed bugs to safe shelters, and one less-volatile component (histamine), which causes their arrestment upon contact. In infested premises, a blend of all six components is highly effective at luring bed bugs into traps. The trapping of juvenile and adult bed bugs, with or without recent blood meals, provides strong evidence that this unique pheromone bait could become an effective and inexpensive tool for bed bug detection and potentially their control.

Sleep tight! Bed bugs rely on chemical cues to locate and arrest in safe shelters. This aggregation pheromone comprises five volatile components (dimethyl disulfide and dimethyl trisulfide, (E)-2-hexenal, (E)-2-octenal, 2-hexanone) that attract bed bugs, and one less-volatile component (histamine) that causes their arrestment upon contact. This blend is highly effective at luring bed bugs into traps in infested premises.
09 Feb 13:25
by Constanze N. Neumann, Tobias Ritter

Charming fluorine: This Essay examines the recent surge in late-stage fluorination reactions and outlines challenges that need to be overcome to increase the impact of modern fluorination methods on the synthesis of complex organofluorine compounds. It is outlined how an improved understanding of the bonding interactions of fluoride could lead to a new class of mild fluorinating reagents and a range of functional-group-tolerant reactions.
09 Feb 11:30
by Eswaraiah Varrla, Claudia Backes, Keith R. Paton, Andrew Harvey, Zahra Gholamvand, Joe McCauley and Jonathan N. Coleman

Chemistry of Materials
DOI: 10.1021/cm5044864

05 Feb 21:10
by Maksym V. Kovalenko, Liberato Manna, Andreu Cabot, Zeger Hens, Dmitri V. Talapin, Cherie R. Kagan, Victor I. Klimov, Andrey L. Rogach, Peter Reiss, Delia J. Milliron, Philippe Guyot-Sionnnest, Gerasimos Konstantatos, Wolfgang J. Parak, Taeghwan Hyeon, Brian A. Korgel, Christopher B. Murray and Wolfgang Heiss

ACS Nano
DOI: 10.1021/nn506223h

03 Feb 20:23
Chem. Commun., 2015, 51,6293-6296
DOI: 10.1039/C4CC09826A, Communication
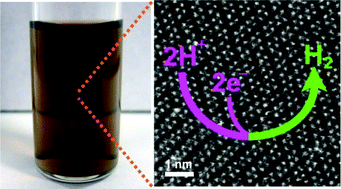
Deepesh Gopalakrishnan, Dijo Damien, Bo Li, Hemtej Gullappalli, Vijayamohanan K. Pillai, Pulickel M. Ajayan, Manikoth M. Shaijumon
Quantum dots of single-/few-layered MoS2 with tunable sizes, obtained through a unique electrochemical exfoliation process, show excellent electrocatalytic activity towards hydrogen evolution reactions.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry

02 Sep 12:31
by Mohamed Eita, Anwar Usman, Ala'a O. El-Ballouli, Erkki Alarousu, Osman M. Bakr, Omar F. Mohammed
Absorbent layers of semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) are now used as material platforms for low-cost, high-performance solar cells. The semiconductor metal oxide nanoparticles as an acceptor layer have become an integral part of the next generation solar cell. To achieve sufficient electron transfer and subsequently high conversion efficiency in these solar cells, however, energy-level alignment and interfacial contact between the donor and the acceptor units are needed. Here, the layer-by-layer (LbL) technique is used to assemble ZnO nanoparticles (NPs), providing adequate PbS QD uptake to achieve greater interfacial contact compared with traditional sputtering methods. Electron injection at the PbS QD and ZnO NP interface is investigated using broadband transient absorption spectroscopy with 120 femtosecond temporal resolution. The results indicate that electron injection from photoexcited PbS QDs to ZnO NPs occurs on a time scale of a few hundred femtoseconds. This observation is supported by the interfacial electronic-energy alignment between the donor and acceptor moieties. Finally, due to the combination of large interfacial contact and ultrafast electron injection, this proposed platform of assembled thin films holds promise for a variety of solar cell architectures and other settings that principally rely on interfacial contact, such as photocatalysis.

Heterojunctions of PbS quantum dots (QDs) acting as sensitizers are coated on a thin layer of ZnO/PAA by the LbL technique to provide a larger interfacial contact compared with films made using the conventional sputtering method. Time-resolved experiments demonstrate that the excited carriers inject from PbS QDs into the ZnO conduction band within 160 fs.
02 Sep 12:30
Nanoscale, 2014, 6,12458-12462
DOI: 10.1039/C4NR03740E, Communication
Takeshi Fujita, Yoshikazu Ito, Yongwen Tan, Hisato Yamaguchi, Daisuke Hojo, Akihiko Hirata, Damien Voiry, Manish Chhowalla, Mingwei Chen
Chemically exfoliated ReS2 nanosheets are demonstrated for hydrogen evolution reactions (HERs) originating from the superlattice phase.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry

29 Aug 10:45
by Chengyang Jiang, Wenyong Liu and Dmitri V. Talapin

Chemistry of Materials
DOI: 10.1021/cm502007d

21 Aug 12:57
by Wan-Ching Hsu, Huanping Zhou, Song Luo, Tze-Bin Song, Yao-Tsung Hsieh, Hsin-Sheng Duan, Shenglin Ye, Wenbing Yang, Chia-Jung Hsu, Chengyang Jiang, Brion Bob and Yang Yang

ACS Nano
DOI: 10.1021/nn503992e

19 Aug 10:20
by Yuho Min, Junghyeok Kwak, Aloysius Soon and Unyong Jeong

Accounts of Chemical Research
DOI: 10.1021/ar500133w

19 Aug 10:18
Faraday Discuss., 2014, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C4FD00145A, Paper
Zhiyuan Zeng, Wen-I. Liang, Ying-Hao Chu, Haimei Zheng
To cite this article before page numbers are assigned, use the DOI form of citation above.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry

12 Aug 09:04
by Mark J. Fernée, Chiara Sinito, Philippe Tamarat and Brahim Lounis

Nano Letters
DOI: 10.1021/nl501448p

12 Aug 08:37
by Yolanda Justo, Laxmi Kishore Sagar, Stijn Flamee, Qiang Zhao, André Vantomme and Zeger Hens

ACS Nano
DOI: 10.1021/nn5037812

12 Aug 08:17
by Chunhung Law, Lukas Miseikis, Stiochko Dimitrov, Pabitra Shakya-Tuladhar, Xiaoe Li, Piers R. F. Barnes, James Durrant, Brian C. O'Regan

Three organic or hybrid photovoltaic technologies are compared with respect to performance and stability under the harsh regime of concentrated light. Although all three technologies show surprisingly high (and linear) photocurrents, and better than expected stability, no golden apples are awarded.
11 Aug 13:55
RSC Adv., 2014, 4,32744-32748
DOI: 10.1039/C4RA04116J, Communication
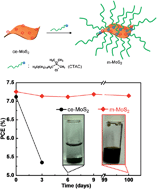
Wenqing Liu, Xi Yang, Yingying Zhang, Mingsheng Xu, Hongzheng Chen
A simple self-assembly procedure was developed for preparing a solution of 2D exfoliated MoS2 sheets with very long-term stability suitable for high-performance solar cell fabrication.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry

11 Aug 11:55
RSC Adv., 2014, 4,34217-34220
DOI: 10.1039/C4RA05035E, Communication
Melissa R. Dewi, Geoffry Laufersky, Thomas Nann
Almost complete ligand exchange and excellent colloidal stability of gold nanoparticles can be achieved by a new solvent extraction based method.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry

11 Aug 11:07
RSC Adv., 2014, 4,36024-36030
DOI: 10.1039/C4RA05979D, Paper
J. C. L. Sousa, M. G. Vivas, J. L. Ferrari, C. R. Mendonca, M. A. Schiavon
In the present study, we report the synthesis of glutathione (GSH) capped CdTe quantum dots (QDs) using the one-pot approach as well as their optical properties.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry

08 Jul 17:49
by Tomas Leijtens, Samuel D. Stranks, Giles E. Eperon, Rebecka Lindblad, Erik M. J. Johansson, Ian J. McPherson, Håkan Rensmo, James M. Ball, Michael M. Lee and Henry J. Snaith

ACS Nano
DOI: 10.1021/nn502115k

18 Jun 18:34
Chem. Commun., 2014, 50,8346-8349
DOI: 10.1039/C4CC00998C, Communication
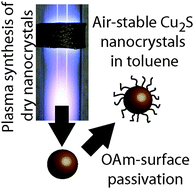
Elijah Thimsen, Uwe R. Kortshagen, Eray S. Aydil
Nonthermal plasmas can produce high quality metal-sulfide nanocrystals in a continuous process without requiring solvents.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry

13 Jun 20:42
Faraday Discuss., 2014, 170,169-179
DOI: 10.1039/C3FD00117B, Paper
Peter Balaz, Matej Balaz, Maria Caplovicova, Anna Zorkovska, Lubomir Caplovic, Miroslav Psotka
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry

13 Jun 20:37
Abstract
A method is presented for using a single laser pulse to transform polymorphic polycrystalline gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) into crystalline nanospheres. Transmission electron microscope analysis of the nominally 60-nm-diameter Au NP starting material and the product suspension confirms the production of slightly smaller particles that exhibit greater crystallinity and feature reduced caliper diameter aspect ratios and anisotropy. Centrifugation followed by ultrasonic resuspension into citrate solution separates the nanospheres from the <15 nm ablation fragments, providing a route to monodisperse spherical crystalline Au NPs.
13 Jun 20:36
by Shuli He, Hongwang Zhang, Hui Xing, Kai Li, Hongfei Cui, Chenguang Yang, Shouheng Sun and Hao Zeng

Nano Letters
DOI: 10.1021/nl501193x

13 Jun 20:30
by Zhenxiao Pan, Iván Mora-Seró, Qing Shen, Hua Zhang, Yan Li, Ke Zhao, Jin Wang, Xinhua Zhong and Juan Bisquert

Journal of the American Chemical Society
DOI: 10.1021/ja504310w

09 Jun 16:43
by Zhijun Ning
Nature Materials.
doi:10.1038/nmat4007
Authors: Zhijun Ning, Oleksandr Voznyy, Jun Pan, Sjoerd Hoogland, Valerio Adinolfi, Jixian Xu, Min Li, Ahmad R. Kirmani, Jon-Paul Sun, James Minor, Kyle W. Kemp, Haopeng Dong, Lisa Rollny, André Labelle, Graham Carey, Brandon Sutherland, Ian Hill, Aram Amassian, Huan Liu, Jiang Tang, Osman M. Bakr & Edward H. Sargent