Shared posts
High-Performance Perovskite Photoanode Enabled by Ni Passivation and Catalysis
Efficient Visible Light Nitrogen Fixation with BiOBr Nanosheets of Oxygen Vacancies on the Exposed {001} Facets
Trinary Layered Double Hydroxides as High-Performance Bifunctional Materials for Oxygen Electrocatalysis
Layered double hydroxides (LDHs) are a family of high-profile layer materials with tunable metal species and interlayer spacing, and herein the LDHs are first investigated as bifunctional electrocatalysts. It is found that trinary LDH containing nickel, cobalt, and iron (NiCoFe-LDH) shows a reasonable bifunctional performance, while exploiting a preoxidation treatment can significantly enhance both oxygen reduction reaction and oxygen evolution reaction activity. This phenomenon is attributed to the partial conversion of Co2+ to Co3+ state in the preoxidation step, which stimulates the charge transfer to the catalyst surface. The practical application of the optimized material is demonstrated with a small potential hysteresis (800 mV for a reversible current density of 20 mA cm−2) as well as a high stability, exceeding the performances of noble metal catalysts (commercial Pt/C and Ir/C). The combination of the electrochemical metrics and the facile and cost-effective synthesis endows the trinary LDH as a promising bifunctional catalyst for a variety of applications, such as next-generation regenerative fuel cells or metal–air batteries.

It is found that incorporating Co into NiFe-layered double hydroxides (LDHs) can significantly improve the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) activity and both the ORR and oxygen evolution reaction activities of trinary NiCoFe-LDHs can be significantly improved by a preoxidation process. This improvement is attributed to the formation of Co3+ in the intralayer, and results in the conductivity improvement of the material.
Solar Fuels: A One-Pot Synthesis of Hydrogen and Carbon Fuels from Water and Carbon Dioxide (Adv. Energy Mater. 7/2015)

A single pot electrolytic synthesis of hydrogen and carbon fuels is achieved through the use of a mixed, hydroxide/carbonate electrolyte, a nickel anode (generating O2), and a nickel or steel cathode. In article number 1401791 Stuart Licht and co-workers report that the generation of hydrogen and carbon fuels is driven with conventional power or efficiently generated from sunlight using solar thermal and electric (CPV) energy as STEP (solar thermal electrochemical process) fuels.
Enhanced Photoelectrochemical Water Oxidation on Bismuth Vanadate by Electrodeposition of Amorphous Titanium Dioxide
[Report] Water photolysis at 12.3% efficiency via perovskite photovoltaics and Earth-abundant catalysts
Enhanced Charge Collection for Splitting of Water Enabled by an Engineered Three-Dimensional Nanospike Array
Reversible Hydrophobic to Hydrophilic Transition in Graphene via Water Splitting Induced by UV Irradiation
Although the reversible wettability transition between hydrophobic and hydrophilic graphene under ultraviolet (UV) irradiation has been observed, the mechanism for this phenomenon remains unclear. In this work, experimental and theoretical investigations demonstrate that the H2O molecules are split into hydrogen and hydroxyl radicals, which are then captured by the graphene surface through chemical binding in an ambient environment under UV irradiation. The dissociative adsorption of H2O molecules induces the wettability transition in graphene from hydrophobic to hydrophilic. Our discovery may hold promise for the potential application of graphene in water splitting.
Scientific Reports 4 doi: 10.1038/srep06450
Graphene Acting as Surface Phase Junction in Anatase–Graphene–Rutile Heterojunction Photocatalysts for H2 Production from Water Splitting
N-doped TiO2 nanotubes coated with a thin TaOxNy layer for photoelectrochemical water splitting: dual bulk and surface modification of photoanodes
DOI: 10.1039/C4EE02169J, Paper
Thin amorphous TaOxNy layer-coated N-doped TiO2 nanotubes successfully serve as a water splitting photoanode.
To cite this article before page numbers are assigned, use the DOI form of citation above.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Photochemistry: A Stable and Efficient Hematite Photoanode in a Neutral Electrolyte for Solar Water Splitting: Towards Stability Engineering (Adv. Energy Mater. 13/2014)

Surface phosphate groups facilitate solar water oxidation on the surface of iron oxide thin films, even in a neutral electrolyte. The method reported by Jae Sung Lee and co-workers in article number 1400476 provides an effective path to the stability engineering of photoelectrodes to employ any electrolyte of choice. Such stability engineering is a critical issue in solution-based energy devices based on hybrid materials with different stability characteristics.
Selective production of hydrogen peroxide and oxidation of hydrogen sulfide in an unbiased solar photoelectrochemical cell
DOI: 10.1039/C4EE01503G, Paper
Hydrogen sulfide was selectively oxidized by O2 to produce hydrogen peroxide and sulfur using a photoelectrochemical cell at zero bias.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Organic photoelectrochemical cells with quantitative photocarrier conversion
DOI: 10.1039/C4EE01775G, Paper
Efficient solar-to-fuel conversion could be a cost-effective way to power the planet using sunlight.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Switchable Charge-Transfer in the Photoelectrochemical Energy-Conversion Process of Ferroelectric BiFeO3 Photoelectrodes
Abstract
Instead of conventional semiconductor photoelectrodes, herein, we focus on BiFeO3 ferroelectric photoelectrodes to break the limits imposed by common semiconductors. As a result of their prominent ferroelectric properties, the photoelectrodes are able to tune the transfer of photo-excited charges generated either in BiFeO3 or the surface modifiers by manipulating the poling conditions of the ferroelectric domains. At 0 V vs Ag/AgCl, the photocurrent could be switched from 0 μA cm−2 to 10 μA cm−2 and the open-circuit potential changes from 33 mV to 440 mV, when the poling bias of pretreatment is manipulated from −8 V to +8 V. Additionally, the pronounced photocurrent from charge injection of the excited surface modifiers could be quenched by switching the poling bias from +8 V to −8 V.

Poling station: The orientation of the BiFeO3 (BFO) band bending at the BFO/electrolyte in polycrystalline BFO photoelectrodes can be switched from upwards to downwards by poling pretreatments of +8 V or −8 V, respectively. It is thus possible to manipulate photoelectrochemical reactions on a single ferroelectric photoelectrode.
Efficient photoelectrochemical hydrogen production from bismuth vanadate-decorated tungsten trioxide helix nanostructures
Article
There is significant research into new composite catalysts for photoelectrochemical water splitting. Here, the authors report a helical bismuth vanadate/tungsten trioxide heterojunction array and show that its structural features yield high photocurrents.
Nature Communications doi: 10.1038/ncomms5775
Authors: Xinjian Shi, Il Yong Choi, Kan Zhang, Jeong Kwon, Dong Yeong Kim, Ja Kyung Lee, Sang Ho Oh, Jong Kyu Kim, Jong Hyeok Park
2-Photon tandem device for water splitting: comparing photocathode first versus photoanode first designs
DOI: 10.1039/C4EE01335B, Analysis
This work analyzes the differences between a 'photoanode first' and a 'photocathode first' 2-photon water splitting device.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Inside Back Cover: Plasmon-Assisted Water Splitting Using Two Sides of the Same SrTiO3 Single-Crystal Substrate: Conversion of Visible Light to Chemical Energy (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 39/2014)

A plasmon-induced water splitting system that operates under irradiation by visible light is described by H. Misawa et al. in their Communication on page 10350 ff. The system uses both sides of the same strontium titanate single-crystal substrate to separate hydrogen and oxygen. The chemical bias is substantially reduced by plasmonic effects because of efficient water oxidation.
Electrochemical and Spectroelectrochemical Characterization of an Iridium-Based Molecular Catalyst for Water Splitting: Turnover Frequencies, Stability, and Electrolyte Effects
A three-dimensional hexagonal fluorine-doped tin oxide nanocone array: a superior light harvesting electrode for high performance photoelectrochemical water splitting
DOI: 10.1039/C4EE01581A, Paper
A hexagonal nanocone array of FTO, a transparent conducting oxide, is excellent in trapping light and in photoelectrochemical water splitting.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Electrodeposition of Ni-doped FeOOH oxygen evolution reaction catalyst for photoelectrochemical water splitting
DOI: 10.1039/C4TA03078H, Paper
Ni-doped FeOOH is tested as a means to alleviate the catalytic bottleneck common in photoelectrochemical water splitting.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Design of High-Efficiency Visible-Light Photocatalysts for Water Splitting: MoS2/AlN(GaN) Heterostructures
An experimental and modeling/simulation-based evaluation of the efficiency and operational performance characteristics of an integrated, membrane-free, neutral pH solar-driven water-splitting system
DOI: 10.1039/C4EE01824A, Paper
An experimental and modeling based evaluation of a solar-hydrogen device that operates in electrolytes buffered at near-neutral pH.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Hierarchical MoS2 microboxes constructed by nanosheets with enhanced electrochemical properties for lithium storage and water splitting
DOI: 10.1039/C4EE01932F, Communication
Hierarchical MoS2 microboxes constructed by ultrathin nanosheets exhibit enhanced electrochemical properties for lithium storage and hydrogen evolution from water.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Improving the Performance of Hybrid Photoanodes for Water Splitting by Photodeposition of Iridium Oxide Nanoparticles
Achieving solar overall water splitting with hybrid photosystems of photosystem II and artificial photocatalysts
Article
Solar water splitting is a promising approach for harvesting solar energy but is hindered by sluggish water oxidation. Here, the authors report a hybrid material containing natural photosystem II and an inorganic photocatalyst and evaluate its overall water splitting performance.
Nature Communications doi: 10.1038/ncomms5647
Authors: Wangyin Wang, Jun Chen, Can Li, Wenming Tian
Tuning the energy band-gap of crystalline gallium oxide to enhance photocatalytic water splitting: mixed-phase junctions
DOI: 10.1039/C4TA03193H, Paper
The rational design and fabrication of mixed-phase oxide junctions is an attractive strategy for photocatalytic applications.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Visible Light-Driven Pure Water Splitting by a Nature-Inspired Organic Semiconductor-Based System
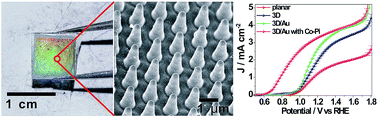
Efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting of nanostructured hematite on a three-dimensional nanoporous metal electrode
DOI: 10.1039/C4TA03578J, Communication
Nanostructured hematites supported on a 3D nanoporous gold electrode exhibited high photoelectrochemical efficiency in water splitting.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Enhancing visible-light photoelectrochemical water splitting through transition-metal doped TiO2 nanorod arrays
DOI: 10.1039/C4TA04254A, Paper
Transition metal doping substantially improves the performance of TiO2 nanorods for photoelectrochemical water splitting in the visible light region.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
The synergetic effect of graphene on Cu2O nanowire arrays as a highly efficient hydrogen evolution photocathode in water splitting
DOI: 10.1039/C4TA03464C, Paper
The graphene modified Cu2O nanowire array demonstrates improved photocurrent density and photostability, attributed to the synergetic effect of graphene.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry