Shared posts
Antimicrobial Peptide Lactoferricin B-Induced Rapid Leakage of Internal Contents from Single Giant Unilamellar Vesicles
[In Depth] Microbes aid cancer drugs
Outer-membrane vesicles from Gram-negative bacteria: biogenesis and functions
Nature Reviews Microbiology 13, 605 (2015). doi:10.1038/nrmicro3525
Authors: Carmen Schwechheimer & Meta J. Kuehn
Outer-membrane vesicles (OMVs) are spherical buds of the outer membrane filled with periplasmic content and are commonly produced by Gram-negative bacteria. The production of OMVs allows bacteria to interact with their environment, and OMVs have been found to mediate diverse functions, including promoting pathogenesis, enabling
Peptide Targeting of an Antibiotic Prodrug toward Phagosome-Entrapped Mycobacteria

Expanding the scope of alkyne-mediated bioconjugations utilizing unnatural amino acids
DOI: 10.1039/C5CC08287K, Communication
The importance of bioconjugates within the field of chemistry drives the need for novel methodologies for their preparation.
To cite this article before page numbers are assigned, use the DOI form of citation above.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Investigational Agents for the Treatment of Gram-Negative Bacterial Infections: A Reality Check

Gene Expression Variability Underlies Adaptive Resistance in Phenotypically Heterogeneous Bacterial Populations

Permeability Barrier of Gram-Negative Cell Envelopes and Approaches To Bypass It

Bacterial Transcription Inhibitor of RNA Polymerase Holoenzyme Formation by Structure-Based Drug Design: From in Silico Screening to Validation

A RIAM/lamellipodin–talin–integrin complex forms the tip of sticky fingers that guide cell migration
Article
The leading edge of migrating cells contains activated integrins associated with growing actin filaments that form ‘sticky fingers’ to guide cell migration. Here, the authors detect a complex of MRL proteins, talin and activated integrins in lamellipodia and filopodia in living cells, comprising the tips of the ‘sticky fingers’.
Nature Communications doi: 10.1038/ncomms9492
Authors: Frederic Lagarrigue, Praju Vikas Anekal, Ho-Sup Lee, Alexia I. Bachir, Jailal N. Ablack, Alan F. Horwitz, Mark H. Ginsberg
Epicatechin gallate, a naturally occurring polyphenol, alters the course of infection with β-lactam-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the zebrafish embryo
Chemoenzymatic Assembly of Bacterial Glycoconjugates for Site-Specific Orthogonal Labeling
Sensing Protein Surfaces with Targeted Fluorescent Receptors
Abstract
Invited for the cover of this issue is the group of David Margulies at the Weizmann Institute of Science (Israel). The image highlights the analogy between fluorescent molecular sensors and a miniaturized camera that can capture changes that occur at the nanoscale and shed light on the structural state of proteins. Read the full text of the article at 10.1002/chem.201502069.

“We believe that the concept of combining a highly specific and a non-specific protein binder on a single molecular platform could open up new possibilities for detecting proteins and/or regulating their functions.” Read more about the story behind the cover in the Cover Profile and about the research itself on page 15981 ff. (DOI: 10.1002/chem.201502069).
Phosphorylation of BlaR1 in Manifestation of Antibiotic Resistance in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Its Abrogation by Small Molecules

Antimicrobial Activity and Toxicity of the Major Lipopeptide Components of Polymyxin B and Colistin: Last-Line Antibiotics against Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria

D-Enantiomeric Peptides that Eradicate Wild-Type and Multidrug-Resistant Biofilms and Protect against Lethal Infections
Through the wall: extracellular vesicles in Gram-positive bacteria, mycobacteria and fungi
Nature Reviews Microbiology 13, 620 (2015). doi:10.1038/nrmicro3480
Authors: Lisa Brown, Julie M. Wolf, Rafael Prados-Rosales & Arturo Casadevall
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are produced by all domains of life. In Gram-negative bacteria, EVs are produced by the pinching off of the outer membrane; however, how EVs escape the thick cell walls of Gram-positive bacteria, mycobacteria and fungi is still unknown. Nonetheless, EVs have been
Enzyme-Instructed Intracellular Molecular Self-Assembly to Boost Activity of Cisplatin against Drug-Resistant Ovarian Cancer Cells
Abstract
Anticancer drug resistance demands innovative approaches that boost the activity of drugs against drug-resistant cancers without increasing the systemic toxicity. Here we show the use of enzyme-instructed self-assembly (EISA) to generate intracellular supramolecular assemblies that drastically boost the activity of cisplatin against drug-resistant ovarian cancer cells. We design and synthesize small peptide precursors as the substrates of carboxylesterase (CES). CES cleaves the ester bond pre-installed on the precursors to form the peptides that self-assemble in water to form nanofibers. At the optimal concentrations, the precursors themselves are innocuous to cells, but they double or triple the activity of cisplatin against the drug-resistant ovarian cancer cells. This work illustrates a simple, yet fundamental, new way to introduce non-cytotoxic components into combination therapies with cisplatin without increasing the systemic burden or side effects.

Cisplatin-boosting nanofibers: The design and synthesis is reported of small peptide precursors that can be cleaved by carboxylesterase (CES) to form peptides that self-assemble in water to form molecular nanofibers. The precursors themselves are innocuous to cells at optimal concentrations, but they double or triple the activity of cisplatin against drug-resistant ovarian cancer cells.
Genetically Encoded Azide Containing Amino Acid in Mammalian Cells Enables Site-Specific Antibody–Drug Conjugates Using Click Cycloaddition Chemistry
Bioorthogonal Enzymatic Activation of Caged Compounds
Abstract
Engineered cytochrome P450 monooxygenase variants are reported as highly active and selective catalysts for the bioorthogonal uncaging of propargylic and benzylic ether protected substrates, including uncaging in living E. coli. observed selectivity is supported by induced-fit docking and molecular dynamics simulations. This proof-of-principle study points towards the utility of bioorthogonal enzyme/protecting group pairs for applications in the life sciences.

The great escape: Engineered cytochrome P450 monooxygenases were used for the removal of propargylic and benzylic ether protecting groups in vitro and in living E. coli. Deprotection resulted in the release of uncaged alcohols, which in this case display fluorescence properties. Such bioorthogonal enzyme/protecting group pairs could provide a means for the selective release of imaging agents or the catalytic activation of prodrugs at their site of action.
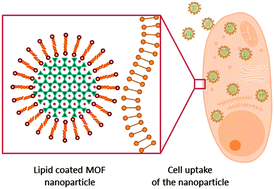
MOF nanoparticles coated by lipid bilayers and their uptake by cancer cells
DOI: 10.1039/C5CC06767G, Communication
We report the synthesis of MOF@lipid nanoparticles as a versatile and powerful novel class of nanocarriers based on metal-organic frameworks (MOFs).
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Biosynthesis of the Novel Macrolide Antibiotic Anthracimycin
Two of a KindThe Biosynthetic Pathways of Chlorotonil and Anthracimycin
Metabolic labeling puts the microbiome under the microscope
Nature Medicine 21, 977 (2015). doi:10.1038/nm.3941
Authors: Graham J Britton & Jeremiah J Faith
Seven years after the launch of the Human Microbiome Project, we still lack sufficient tools to visualize the microbiome in a living host. A new study provides experimental tools to label and track live anaerobic bacteria in the microbial communities in the mouse gut and beyond.
A Rationally Designed Upconversion Nanoprobe for in Vivo Detection of Hydroxyl Radical
Bacteria, inflammation and cancer
Nature Reviews Immunology 15, 528 (2015). doi:10.1038/nri3899
Author: Jeffrey Pollard
Jeffrey Pollard describes a 2003 study by Enzler et al. that identified the immune response against bacteria as preventing chronic inflammation-associated tumour development.