wjzmy1994
Shared posts
[ASAP] Predictable Particle Engineering: Programming the Energy Level, Carrier Generation, and Conductivity of Core–Shell Particles
[ASAP] Inter-Backbone Charge Transfer as Prerequisite for Long-Range Conductivity in Perylene Bisimide Hydrogels
Perovskite Solar Cells: All-Carbon-Electrode-Based Endurable Flexible Perovskite Solar Cells (Adv. Funct. Mater. 11/2018)

A durable flexible perovskite solar cell that employs graphene as transparent anode and carbon nanotubes as cathode is successfully developed by Ning Wang, Kaili Jiang, Hong Lin, Zhanhu Guo, and co-workers in article number 1706777. All-carbon-electrode-based devices exhibit promising efficiency, excellent flexibility, and stability, providing a new avenue for construction of cheap and large-scale flexible perovskite solar cells.
From Nanostructural Evolution to Dynamic Interplay of Constituents: Perspectives for Perovskite Solar Cells
Abstract
Moving away from the high-performance achievements in organometal halide perovskite (OHP)-based optoelectronic and photovoltaic devices, intriguing features have been reported in that photocarriers and mobile ionic species within OHPs interact with light, electric fields, or a combination of both, which induces both spatial and temporal changes of optoelectronic properties in OHPs. Since it is revealed that the transport of photocarriers and the migration of ionic species are affected not only by each other but also by the inhomogeneous character, which is a consequence of the route selected to deposit OHPs, understanding the nanostructural evolution during OHP deposition, in terms of the resultant structural defects, electronic traps, and nanoscopic charge behaviors, will be valuable. Investigation of the film-growth mechanisms and strategies adopted to realize OHP films with less-defective large grains is of central importance, considering that single-crystalline OHPs have exhibited the most beneficial properties, including carrier lifetimes. Critical factors governing the behavior of photocarriers, mobile ionic species, and nanoscale optoelectronic properties resulting from either or all of them are further summarized, which may potentially limit or broaden the optoelectronic and photovoltaic applications of OHPs. Through inspection of the recent advances, a comprehensive picture and future perspective of OHPs are provided.

With giant steps regarding organometal halide perovskite (OHP)-based optoelectronic and photovoltaic devices having been made, OHPs are being driven toward applications beyond photovoltaics. Recent progress regarding the various characteristics of OHPs and their impact on photovoltaic devices are reviewed, from microstructural evolution coupled with nanostructural/electronic disorder to photoinduced charge-carrier dynamics; the implications for potential applications are also outlined.
Stable hybrid organic-inorganic halide perovskites for photovoltaics from ab initio high-throughput calculations
DOI: 10.1039/C7TA08992A, Paper
By means of high-throughput first-principles calculations, we screen a large number of hypothetical hybrid perovskite compounds by stability, band gap and effective mass to find the best perovskites for photovoltaics.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Bilateral Interface Engineering toward Efficient 2D–3D Bulk Heterojunction Tin Halide Lead-Free Perovskite Solar Cells

HyPe-2017: A Discussion Meeting on Hybrid Perovskites
Complex Refractive Indices of Cesium–Formamidinium-Based Mixed-Halide Perovskites with Optical Band Gaps from 1.5 to 1.8 eV

[ASAP] Efficient and Selective Photocatalytic Oxidation of Benzylic Alcohols with Hybrid Organic–Inorganic Perovskite Materials

Highly Efficient Tandem Organic Solar Cell Enabled by Environmentally Friendly Solvent Processed Polymeric Interconnecting Layer
Abstract
In the field of organic solar cells (OSCs), tandem structure devices exhibit very attractive advantages for improving power conversion efficiency (PCE). In addition to the well researched novel pair of active layers in different subcells, the construction of interconnecting layer (ICL) also plays a critical role in achieving high performance tandem devices. In this work, a new way of achieving environmentally friendly solvent processed polymeric ICL by adopting poly[(9,9-bis(3′-(N,N-dimethylamino)propyl)-2,7-fluorene)-alt-5,5′-bis(2,2′-thiophene)-2,6-naphthalene-1,4,5,8-tetracaboxylic-N,N′-di(2-ethylhexyl)imide] (PNDIT-F3N) blended with poly(ethyleneimine) (PEI) as the electron transport layer (ETL) and PEDOT:PSS as the hole transport layer is reported. It is found that the modification ability of PNDIT-F3N on PEDOT can be linearly tuned by the incorporation of PEI, which offers the opportunity to study the charge recombination behavior in ICL. At last, tandem OSC with highest PCE of 12.6% is achieved, which is one of the best tandem OSCs reported till now. These results offer a new selection for constructing efficient ICL in high performance tandem OSCs and guide the way of design new ETL materials for ICL construction, and may even be integrated in future printed flexible large area module device fabrication with the advantages of environmentally friendly solvent processing and thickness insensitivity.

A new polymeric interconnecting layer (ICL) based on poly[(9,9-bis(3′-(N,N-dimethylamino)propyl)-2,7-fluorene)-alt-5,5′-bis(2,2′-thiophene)-2,6-naphthalene-1,4,5,8-tetracaboxylic-N,N′-di(2-ethylhexyl)imide]: poly(ethyleneimine)/PEDOT:PSS is developed and applied for the fabrication of high performance tandem organic solar cells (OSCs). Tandem OSCs employing this ICL achieve a high power conversion efficiency of 12.6% with ICL thickness of 60 nm and even reach to 11.3% with ICL thickness of 140 nm.
Characterization of the Valence and Conduction Band Levels of n = 1 2D Perovskites: A Combined Experimental and Theoretical Investigation
Abstract
This study presents a combined experimental and theoretical study of the electronic structure of two 2D metal halide perovskite films. Ultraviolet and inverse photoemission spectroscopies are performed on solution-processed thin films of the n = 1 layered perovskite butylammonium lead iodide and bromide, BA2PbI4 and BA2PbBr4, characterized by optical absorption and X-ray diffraction, to determine their valence and conduction band densities of states, transport gaps, and exciton binding energies. The electron spectroscopy results are compared with the densities of states determined by density functional theory calculations. The remarkable agreement between experiment and calculation enables a detailed identification and analysis of the organic and inorganic contributions to the valence and conduction bands of these two hybrid perovskites. The electron affinity and ionization energies are found to be 3.1 and 5.8 eV for BA2PbI4, and 3.1 and 6.5 eV for BA2PbBr4. The exciton binding energies are estimated to be 260 and 300 meV for the two materials, respectively. The 2D lead iodide and bromide perovskites exhibit significantly less band dispersion and a larger density of states at the band edges than the 3D analogs. The effects of using various organic ligands are also discussed.

Understanding the density of electronic states (DOS) in 2D metal halide perovskites is a crucial step in the investigation of the fundamental properties of these materials. This combined experimental–theoretical study via direct and inverse photoemission spectroscopy and density functional theory calculations maps out the various contributions from organic and inorganic constituents to the DOS of the materials.
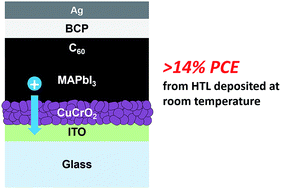
Room-temperature fabrication of a delafossite CuCrO2 hole transport layer for perovskite solar cells
DOI: 10.1039/C7TA09494A, Paper
A delafossite CuCrO2 hole transport layer deposited at room temperature from a nanoparticle suspension is used in efficient perovskite cells.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
Strong Depletion in Hybrid Perovskite p–n Junctions Induced by Local Electronic Doping
Abstract
A semiconductor p–n junction typically has a doping-induced carrier depletion region, where the doping level positively correlates with the built-in potential and negatively correlates with the depletion layer width. In conventional bulk and atomically thin junctions, this correlation challenges the synergy of the internal field and its spatial extent in carrier generation/transport. Organic–inorganic hybrid perovskites, a class of crystalline ionic semiconductors, are promising alternatives because of their direct badgap, long diffusion length, and large dielectric constant. Here, strong depletion in a lateral p–n junction induced by local electronic doping at the surface of individual CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite nanosheets is reported. Unlike conventional surface doping with a weak van der Waals adsorption, covalent bonding and hydrogen bonding between a MoO3 dopant and the perovskite are theoretically predicted and experimentally verified. The strong hybridization-induced electronic coupling leads to an enhanced built-in electric field. The large electric permittivity arising from the ionic polarizability further contributes to the formation of an unusually broad depletion region up to 10 µm in the junction. Under visible optical excitation without electrical bias, the lateral diode demonstrates unprecedented photovoltaic conversion with an external quantum efficiency of 3.93% and a photodetection responsivity of 1.42 A W−1.

Strong charge depletion in a lateral perovskite nanosheet p–n junction is reported with a large depletion width (>10 µm) and a high built-in potential (≈0.5 eV) through local electronic doping at the surface of individual CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite nanosheets. 2D electrostatics imaging further reveals a thickness dependence of the depletion width in the perovskite p–n junctions.
Temperature-Dependent Photoluminescence of Cesium Lead Halide Perovskite Quantum Dots: Splitting of the Photoluminescence Peaks of CsPbBr3 and CsPb(Br/I)3 Quantum Dots at Low Temperature
wjzmy1994CsPbBr3/CsPbI3量子点光致发光
Understanding the Impact of Thiophene/Furan Substitution on Intrinsic Charge-Carrier Mobility
wjzmy1994呋喃噻吩
Wearable Electronics: Wearable Large-Scale Perovskite Solar-Power Source via Nanocellular Scaffold (Adv. Mater. 42/2017)
wjzmy1994好牛

In article number 1703236, Fengyu Li, Yanlin Song, and co-workers report hysteresis-free, flexible, and large-scale perovskite solar cells with recorded photoelectric conversion efficiencies of 12.3% for a 1 cm2 single chip and 8.4% for a 24 cm2 solar module. This is the first time that a wearable solar power source that can supply power for multifunction electronic devices with a variety of body movements is fabricated practically.