08 Aug 07:30
by Jingli Wang, Qian Yao, Chun-Wei Huang, Xuming Zou, Lei Liao, Shanshan Chen, Zhiyong Fan, Kai Zhang, Wei Wu, Xiangheng Xiao, Changzhong Jiang, Wen-Wei Wu

High-performance MoS2 transistors are developed using atomic hexagonal boron nitride as a tunneling layer to reduce the Schottky barrier and achieve low contact resistance between metal and MoS2. Benefiting from the ultrathin tunneling layer within 0.6 nm, the Schottky barrier is significantly reduced from 158 to 31 meV with small tunneling resistance.
08 Aug 07:30
by Li Nian, Ke Gao, Feng Liu, Yuanyuan Kan, Xiaofang Jiang, Linlin Liu, Zengqi Xie, Xiaobin Peng, Thomas P. Russell, Yuguang Ma

Highly efficient electron extraction is achieved by using a photoconductive cathode interlayer in inverted ternary organic solar cells (OSCs) where a near-IR absorbing porphyrin molecule is used as the sensitizer. The OSCs show improved device performance when the ratio of the two donors varies in a large region and a maximum power conversion efficiency up to 11.03% is demonstrated.
08 Aug 03:05
by Xiaozhou Che, Chin-Lung Chung, Xiao Liu, Shu-Hua Chou, Yi-Hung Liu, Ken-Tsung Wong, Stephen R. Forrest

Donor–acceptor–acceptor′ small-molecule donors are synthesized to investigate regioisomeric effects on organic photovoltaic device performance. Cross-conjugation in 2-((7-(N-(2-ethylhexyl)-benzothieno[3,2-b]thieno[3,2-d]pyrrol-2-yl)benzo[c][1,2,5]thiadiazol-4-yl)methylene)malononitrile leads to an increased open-circuit voltage compared with its isomer 2-((7-(N-(2-ethylhexyl)-benzothieno[3,2-b]thieno[2,3-d]pyrrol-2-yl)benzo[c][1,2,5]thiadiazol-4-yl)methylene)malononitrile. A correlation is then established between molecular conjugation length and orbital energies, and hence open-circuit voltage.
02 Aug 06:09
by Cauê F. Ferreira, Eduardo E. Pérez-Cordero, Khalil A. Abboud and Daniel R. Talham

Chemistry of Materials
DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.6b02208

02 Aug 06:08
by Kai Wang, Mehdi Azouz, Maxime Babics, Federico Cruciani, Tomasz Marszalek, Qasim Saleem, Wojciech Pisula and Pierre M. Beaujuge

Chemistry of Materials
DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.6b01763

28 Jul 14:47
by Weichao Chen, Manjun Xiao, Liangliang Han, Jidong Zhang, Huanxiang Jiang, Chuantao Gu, Wenfei Shen and Renqiang Yang

ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b06070

28 Jul 14:46
by Wang-Chao Chen, Fan-Tai Kong, Zhao-Qian Li, Jia-Hong Pan, Xue-Peng Liu, Fu-Ling Guo, Li Zhou, Yang Huang, Ting Yu and Song-Yuan Dai

ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b04411

27 Jul 00:31
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016, 18,23174-23183
DOI: 10.1039/C6CP01994C, Paper
Lei Zhang, Ming-Gang Ju, WanZhen Liang
The degradation mechanism of perovskite materials when exposed to moisture and sunlight has been fully explored.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry

27 Jul 00:31
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016, 18,28428-28433
DOI: 10.1039/C6CP02971J, Paper
Som Sarang, Hidetaka Ishihara, Yen-Chang Chen, Oliver Lin, Ajay Gopinathan, Vincent C. Tung, Sayantani Ghosh
The low temperature anomalous spectroscopic properties of hybrid perovskite thin films were analyzed and a theoretical formalism was developed to quantify perovskite film quality.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry

26 Jul 00:10
Chem. Commun., 2016, 52,11203-11206
DOI: 10.1039/C6CC05737C, Communication
Paifeng Luo, Shengwen Zhou, Zhaofan Liu, Wei Xia, Lin Sun, Jigui Cheng, Chenxi Xu, Yingwei Lu
We present a new transformation route from PbS to CH3NH3PbI3 for the facile preparation of perovskites with all kinds of shapes via vapor-assisted chemical bath deposition (VACBD). As such, curved and large-area CH3NH3PbI3 films with high quality are successfully achieved, which are suitable for the manufacturing scale-up of perovskite solar cells.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry

25 Jul 00:01
by Jillian Epstein, Wee-Liat Ong, Christopher J. Bettinger and Jonathan A. Malen

ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b06338

25 Jul 00:01
by Fei Li, Zhiguo Xia and Quanlin Liu

The Journal of Physical Chemistry C
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b05894

25 Jul 00:00
by Wiley A. Dunlap-Shohl, Robert Younts, Bhoj Gautam, Kenan Gundogdu and David B. Mitzi

The Journal of Physical Chemistry C
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b05406

22 Jul 06:08
by Jiaju Xu, Yulong Wang, Haiquan Shan, Yiwei Lin, Qian Chen, V. A. L. Roy and Zongxiang Xu

ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b04817

22 Jul 06:07
by Irene Lucas, David Ciudad, Manuel Plaza, Sandra Ruiz-Gómez, Claudio Aroca and Lucas Pérez

ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b02577

22 Jul 06:05
Publication date: 30 September 2016
Source:Journal of Power Sources, Volume 327
Author(s): Jinlei Xu, Shufang Wu, Jin Hyok Ri, Jingpeng Jin, Tianyou Peng
A novel bilayer brookite TiO2 film photoanode consisting of quasi nanocube film as underlayer and rice-like submicrometer particle film as overlayer are fabricated for improving the photovoltaic properties of the pure brookite-based dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs). The brookite TiO2 nanocubes have a mean size of ∼50 nm, and the brookite TiO2 rice-like particles have diameter of ∼600 nm and length of ∼1100 nm. An optimal photovoltaic conversion efficiency of 5.51% is obtained from the bilayer brookite-based solar cell, with ∼41% improvement in the efficiency as compared to the single brookite nanocube film-based one (3.91%) under AM 1.5G one sun irradiation. The bilayer brookite-based solar cell shows not only reduced charge recombination and dark current, but also prolonged electron lifetime compared to the single brookite nanocube film-based one. All these lead to a higher photocurrent and voltage, and then to the improved efficiency of the brookite-based solar cell. The present results demonstrate a clear advance towards efficient improvement of the photovoltaic performance of pure brookite-based solar cells.
Graphical abstract

21 Jul 00:33
by Igal Levine, Pabitra K. Nayak, Jacob Tse-Wei Wang, Nobuya Sakai, Stephan Van Reenen, Thomas M. Brenner, Sabyasachi Mukhopadhyay, Henry J. Snaith, Gary Hodes and David Cahen

The Journal of Physical Chemistry C
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b04233

21 Jul 00:33
by Cory J. Flynn, Shannon M. McCullough, Lesheng Li, Carrie L. Donley, Yosuke Kanai and James F. Cahoon

The Journal of Physical Chemistry C
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b06593

20 Jul 05:45
by Wenxia Guo, Zhonglin Du, Qingfei Zhao, Hua Zhang and Xinhua Zhong

The Journal of Physical Chemistry C
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b05211

18 Jul 00:52
by Hee Chang Yoon, Heejoon Kang, Soyoung Lee, Ji Hye Oh, Heesun Yang and Young Rag Do

ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b05468

18 Jul 00:51
by S. Kumar and A. Dhar

ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b06878

18 Jul 00:51
by Haowei Wang, Yishan Wang, Bo He, Weile Li, Muhammad Sulaman, Junfeng Xu, Shengyi Yang, Yi Tang and Bingsuo Zou

ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b03198

18 Jul 00:50
by Xiaorui Jia, Lianping Zhang, Qun Luo, Hui Lu, Xueyuan Li, Zhongzhi Xie, Yongzhen Yang, Yan-Qing Li, Xuguang Liu and Chang-Qi Ma

ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b03724

18 Jul 00:49
by Wenjun Zhang, Changjian Song, Xiaohui Liu and Junfeng Fang

ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b04955

18 Jul 00:46
by Min Chul Suh, So-Ra Park, Ye Ram Cho, Dong Heon Shin, Pil-Gu Kang, Dong A Ahn, Hyung Suk Kim and Chul-Bae Kim

ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b03281

18 Jul 00:45
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016, 18,22628-22635
DOI: 10.1039/C6CP01278G, Paper
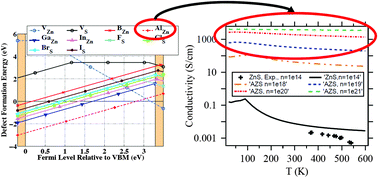
Alireza Faghaninia, Kunal Rajesh Bhatt, Cynthia S. Lo
Wurtzite ZnS alloyed with Al is predicted to be the best transparent conducting sulfide (with +3000 S cm-1 conductivity) among B, Al, Ga, In, F, Cl, Br, I as alloying candidates.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry

14 Jul 08:29
by Keng-Ku Liu, Sirimuvva Tadepalli, Gayatri Kumari, Progna Banerjee, Limei Tian, Prashant K. Jain and Srikanth Singamaneni

The Journal of Physical Chemistry C
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b00955

13 Jul 00:55
by Fangfang Wang, Xiaoning Li, Xiaofeng Yin, Zhengping Fu and Yalin Lu

The Journal of Physical Chemistry C
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b03147

12 Jul 00:33
Chem. Commun., 2016, 52,9933-9936
DOI: 10.1039/C6CC04283J, Communication
Duo Xu, Dong Liu, Tao Xie, Yue Cao, Jun-Gang Wang, Zhi-jun Ning, Yi-Tao Long, He Tian
We demonstrate the electron transfer between gold nanoparticles and perovskite CH3NH3PbI3 at a single nanoparticle level by plasmon resonance Rayleigh scattering spectroscopy.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry

09 Jul 09:32
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016, 18,27073-27077
DOI: 10.1039/C6CP03316D, Communication
Wei-Jie Chi, Ping-Ping Sun, Ze-Sheng Li
meta-Substitution is more beneficial to reduce HOMO levels compared with ortho- and para-substitution, while the hole mobility can be improved by ortho-substitution.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry